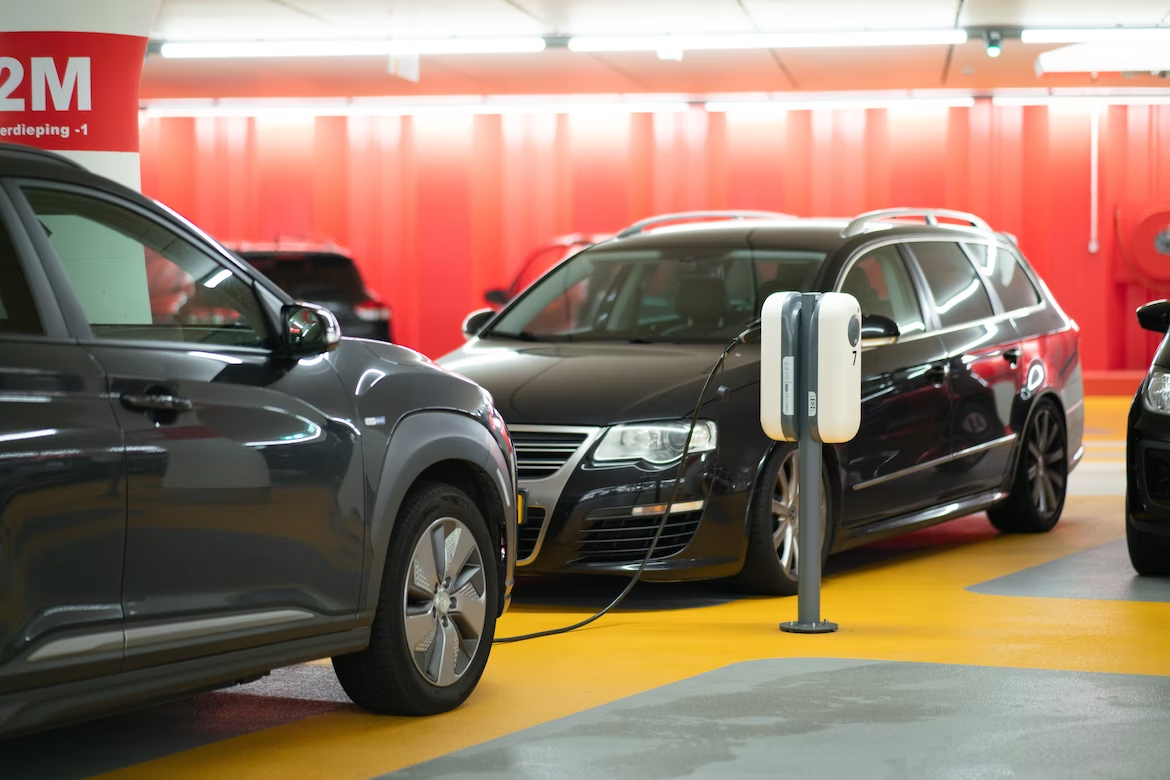


Electric automobiles are becoming more and more popular. As more automakers develop and roll out new models, it is easy to picture a future in which all vehicles are electric. The range of electric cars, which is mostly dependent on the capacity of their batteries, is what makes them economically viable.
How is so much energy kept in reserve?
Electric automobiles need to have compact batteries, regular, quick recharges, and enough capacity to get you where you need to go.
This article examines the most popular battery types for electric vehicles, as well as their possible capacities and typical lifespans.
Which Batteries Can Be Found in Electric Cars?
Battery technology has advanced significantly during the last 40 years. We’ve come a long way from lead-acid batteries in the past thanks to the push for more environmentally friendly energy. Let’s examine the two battery kinds that are currently most frequently used in electric cars.
Battery Types: Lithium-ion
In contemporary electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries are the norm. The most energy-dense of the six primary lithium chemistry types is generally used in automobiles. This often involves the use of lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) or lithium nickel cobalt oxide (NCA). Check out this interesting blog post on Lithium battery types for more details.
There are three different forms of cell housing: pouch-style, prismatic, and cylindrical. All three are present in modern EVs, and each has advantages and disadvantages.
For instance, Tesla selects cylindrical batteries due to their dependability and longevity. Numerous lithium-ion cells from their battery packs are kept underneath the inside carriage of the car. The highest energy-density battery in the world is these lithium-ion battery cells. In contrast to other varieties, they are however heavy.
Hybrid Nickel-Metal Batteries
The 1987 development of nickel-metal hybrid batteries allowed for the creation of hybrid automobiles. The creation of a novel cathode material made of silicon, nickel, cobalt, lanthanum, and nickel caused this to happen. Even after 4,000 charge/recharge cycles, the cell was able to maintain 84% of its charge capacity thanks to the new formula.
The nickel-metal hybrid batteries were later able to preserve substantially more energy density than lead-acid batteries thanks to further advancements in battery chemistry.
Nickel-metal hybrid batteries are now mostly used in hybrid autos. Because of their safety and great energy output, they are well-liked. Additionally, unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium batteries’ level of charge has less of an impact on their output.
But the cost of nickel-metal hybrid batteries is high. Additionally, they require more cooling and have higher self-discharge rates. The Honda Insight, Toyota Prius, and Honda Civic Hybrid all use this kind of electric vehicle battery.
How Much Capacity Does a Battery in an Electric Car Have?
As you might have anticipated, several variables, such as the battery types utilized and the vehicle itself, affect the energy capacity of an electric car battery. The larger the battery capacity, measured in kWh, the more kilometers the car can go before needing to be recharged.
So, a battery for an electric vehicle can have a capacity in the order of kWh. For comparison, a Nissan Leaf has a 40-kilowatt-hour battery and can travel 149 miles between charges, whereas the Tesla Model S and X have a 100 kWh battery and can travel 300 miles between charges.
How long does an electric car’s battery last?
Many individuals are debating buying one of these fuel-efficient cars, so you may be wondering how long the batteries will last. The batteries that run the car are ultimately what determine its quality.
The battery’s treatment, charge and discharge cycles, and operating temperatures all have an impact on how long the battery will last. To maintain the batteries running as efficiently as possible and prolong their life, many cars use sophisticated battery management systems, heating systems, and even cooling systems.
What Happens To EV Batteries After Use?
Where do all of the batteries for electric vehicles go if they ultimately die? Makers would repurpose them and create new batteries in an ideal world. The batteries must first be crushed at specialized facilities before being broken down with chemicals or heat and the valuable materials extracted.
Sadly, because the world is not perfect, only a small portion of rechargeable batteries get recycled. The biggest problem? Logistics of labor and shipping. Actually, it takes more time and resources to ship these lithium-ion batteries than it does to mine new materials. The lack of profitability is the root of the issue. However, this is being researched on right currently and will be resolved once lithium batteries take over as our cars’ main power source.
Are EV Batteries Using New Technology?
Improvements in EV batteries have been accelerating, and they could also find a solution to the recycling issue.
Everything is always being improved, from energy efficiency and production costs to safety. The ultimate goal is to increase battery capacity so that it can safely store energy for as long as feasible.
Batteries for electric vehicles are getting better.
We’ve made significant strides in battery technology, and now EVs are both reliable and affordable. This market is dominated by lithium-ion batteries, and this will probably remain the case for a very long time.
Every battery has advantages and disadvantages, but recent advancements and ideas in the field of electric car batteries may be the answer to many issues currently facing the sector.



One thought on “Which Batteries Are Employed in Electric Vehicles?”
Correct.