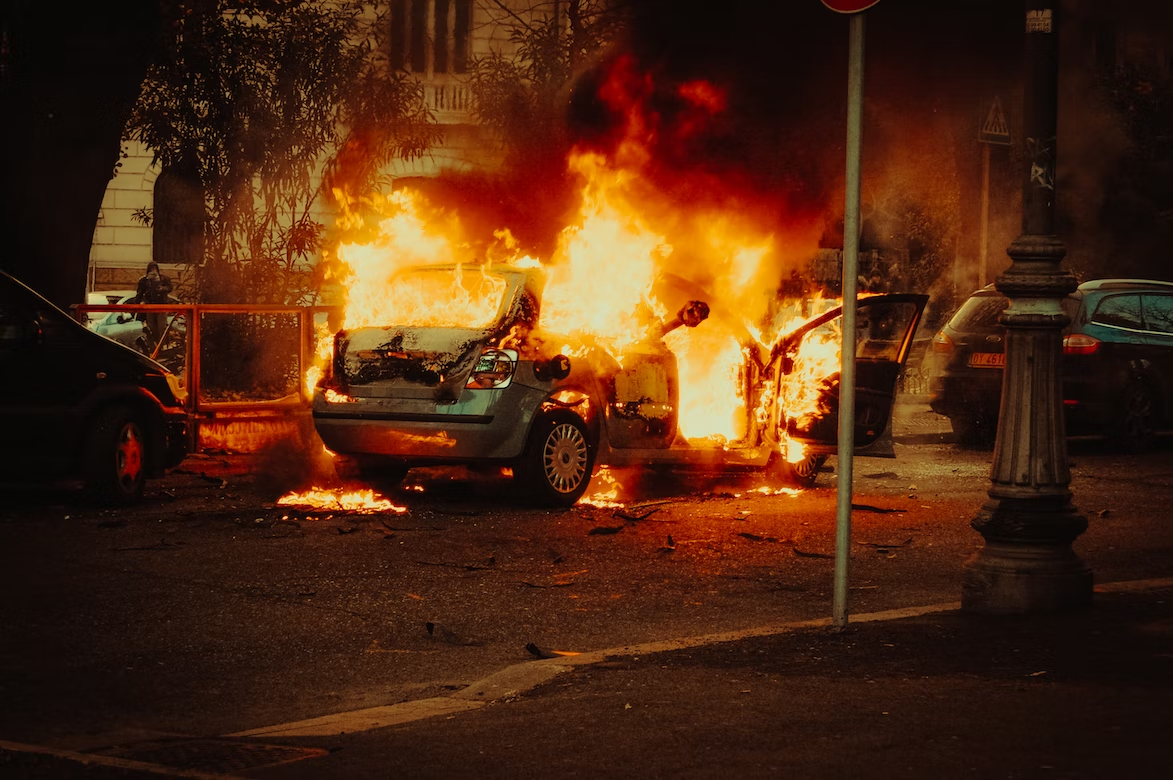
Lithium-ion batteries are naturally flammable and particularly sensitive to high temperatures. These battery packs often degrade considerably more quickly in the heat than they otherwise would. A malfunctioning lithium-ion battery pack will catch fire and can result in significant damage. This calls for quick action and the creation of battery safety laws.
Battery safety features
Battery safety features mentioned below have been incorporated into the design of lithium-ion cells to help you reap the several Lithium ion battery benefits without any worries.
A. Vents with pressure sensors
Batteries need a metal outer wall with a pressure-sensitive vent hole since they are under pressure. This vent will let out excess pressure if the battery is at risk of overheating and bursting due to overpressure (pressure buildup at 3,000 kPa), which will stop other cells in the rechargeable battery from catching fire.
B. The separator functions as a fuse
A polyolefin separator, which is commonly used in lithium-ion batteries and has exceptional chemical stability, excellent mechanical properties, and a competitive price, is used. The cell becomes a fuse as soon as it begins to heat up. When the core reaches 130°C (266°F), the separator melts under intense heat, stopping the movement of ions. This action immediately turns off the cell.
The heat from the malfunctioning cell might have crossed the thermal runaway threshold and ignited without this safeguard.
C. Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC)
To prevent the battery from overheating, this switch protects it from surges in current. Like other chemistries, lithium-ion cells discharge themselves. The loss of a battery’s stored charge without the electrodes or an external circuit connected is known as self-discharge. This is brought on by internal chemical reactions in the cell. With aging, cycling, and high temperatures, cell self-discharge increases.
Elevated self-discharge may cause temperatures to rise; if this happens, a Thermal Runaway, also referred to as “venting with flame,” may occur. Since little heat is generated, a mild short won’t result in a thermal runaway because little energy is released.
However, there may be a substantial electrical short and a sizable current could flow between the positive and negative plates if the cell is damaged in some manner and impurities get inside. The energy stored in the battery is released in a couple of milliseconds when the temperature increases suddenly. To create battery packs, thousands of cells are crushed together.
The next cell could become thermally unstable due to heat generated by a failing cell during a thermal runaway. This chain reaction might destroy the entire pack in a couple of seconds.
What causes fire Issues in Lithium batteries?
Now that we are aware of the causes of lithium-ion battery fires, let’s examine some of the potential scenarios:
1. Manufacturing Errors
Metallic impurities (production flaws) may infiltrate into the lithium-ion cell during the manufacturing process. Batteries must be manufactured in cleanrooms that must adhere to strict regulations.
Another flaw can be the thinned separators, which could be harmful when used. Before being sold, cells must pass rigorous quality-control inspections and validation.
2. Design errors
Automobile manufacturers strive to make their vehicles as svelte and trim as possible while yet offering the highest levels of performance and range. By cramming high-capacity cells into a smaller body, makers of battery packs are forced to develop compact designs, which compromise otherwise well-built batteries.
The electrodes or the separator may become damaged if the design is compromised. Both of which might cause a short circuit. Furthermore, as the flammable electrolyte heats up, a defective cooling system or vent might increase battery temperatures.
If left unchecked, it can trigger a series of cell failures, raising the battery’s temperature and increasing the risk of an uncontrollable explosion.
3. Unusual or Incorrect Use
The battery may explode due to external circumstances like being kept very close to a heat source or a fire. It is inevitable that piercing the battery pack, whether on purpose or by accident, would result in a short circuit and the battery catching fire. Because of this, unlawful battery pack disassembly in electric vehicles causes the warranty to expire.
Users are encouraged to only have their batteries inspected and repaired at facilities approved by the automobile manufacturer. The battery could be harmed even by high-voltage charging or excessive draining.
4. Charger Problems
The battery might be harmed by using chargers with insufficient insulation. The charger may fail if it shorts out or overheats close to the battery.
Although lithium-ion batteries include safeguards to prevent overcharging, utilizing unauthorized chargers can harm the battery over time.
5. Poor-quality parts
Using low-quality components is one of the leading reasons for battery failures, along with manufacturing flaws. Battery prices are falling as a result of increased competition, which is leading manufacturers of batteries to make questionable decisions. The likelihood of a battery failure rises when cheap electronics, such as the battery management system, are used.
For batteries to operate safely and effectively, a battery management system is essential. It guards against the battery pack using it outside of its permitted functioning range. An electric vehicle’s or energy storage system’s batteries are a high-value component, therefore it’s critical to invest in a smart battery management system that can spot cell problems right once and stop the battery from blowing up.
What should one do if a battery starts to burn?
Try moving the gadget away from combustible items and switching off the current supply if you see the lithium-ion battery beginning to heat up. If you’re driving an electric vehicle, you should get out of there right away and never try to put out lithium battery fires on your own. Dial 911 instead because your health and safety are much more crucial.
A regular ABC or BC dry chemical fire extinguisher must be used in the event of a fire because these are regarded as Class B fires. Lithium-ion batteries do not, contrary to popular belief, really contain any lithium metal. You shouldn’t use a Class D fire extinguisher since they don’t and for that reason.
There are also modern techniques for putting out lithium fires. A chemically exfoliated form of vermiculite is dispersed as a mist by a fire-extinguishing agent called aqueous vermiculite dispersion (AVD). Larger lithium-ion flames, such as those used in EVs or ESS, may need to burn out, though. While using copper-infused water is efficient, it is also expensive.
Even in cases of severe lithium-ion fires, battery safety experts advise using water. This kind of fire can smolder for several days, so it’s critical to keep them isolated from flammable substances and curtail their growth.
Making Batteries Safe
Battery safety should be prioritized above anything else by battery pack manufacturers. Making lithium-ion batteries “smart” will make them safer. Using Battery Management System (BMS), we can not only diagnose but also forecast improper battery usage or performance by incorporating a layer of intelligence into the batteries. This will enable us to act quickly, avoid system damage, and guarantee battery safety.